GES Modules
Quick Modeling
Quick Modeling include 2 methods: quick stochastic modeling and quick deterministic modeling. Both methods simplify geological modeling workflow, and employ numerous algorithms to automatically import data, estimate modeling parameters, and optimize modeling results. The reliability of modeling results has been widely tested, and are proven to match well data and geology.
Quick Stochastic Modeling
Quick Stochastic Modeling is also called One-Button modeling, which is a fully automated modeling method, the grid is Conner point grid. There are 4 steps in one button stochastic modeling, fault modeling, horizon modeling, facies modeling and petrophysics modeling, all functions are concentrated in one interface, it’s very easily to use. And it suits for whole oil development stage. One Button geological modeling significantly simplifies steps and improve work efficiency.
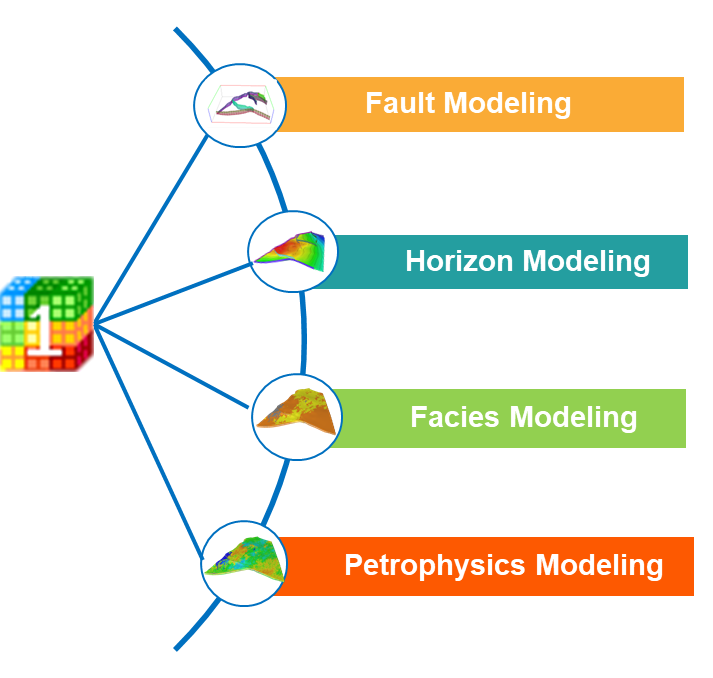
Fig. Quick stochastic modeling workflow
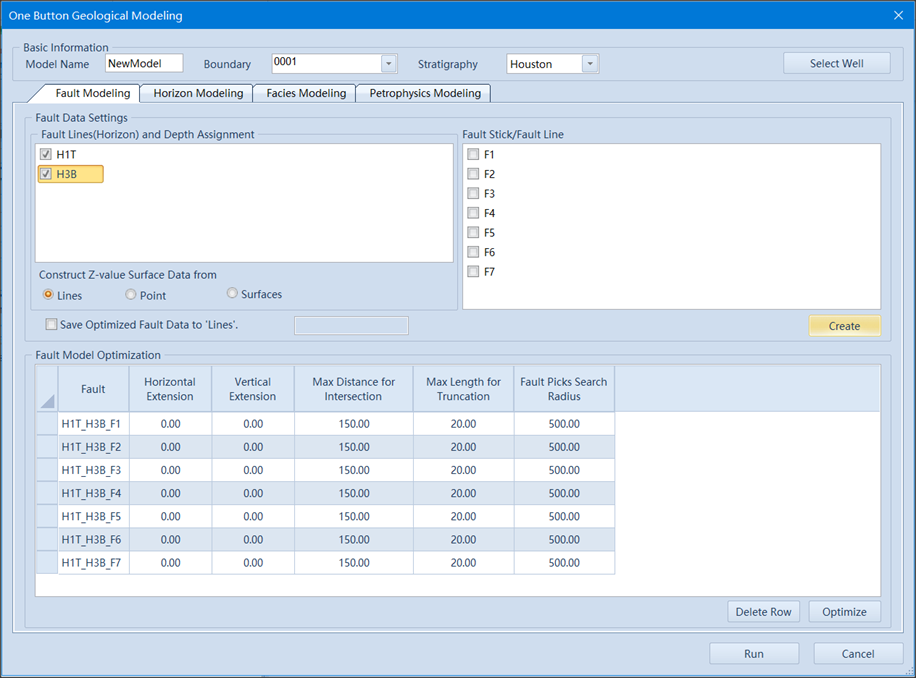
Fig. Quick stochastic modeling interface
One Button stochastic modeling is a fully automated modeling method. automation rans through the entire process of one button stochastic modeling, automatically input data, automatically process data, automatically generate model, in a word, automation is the key word of one button modeling. GES can handle multiple faults simultaneously.
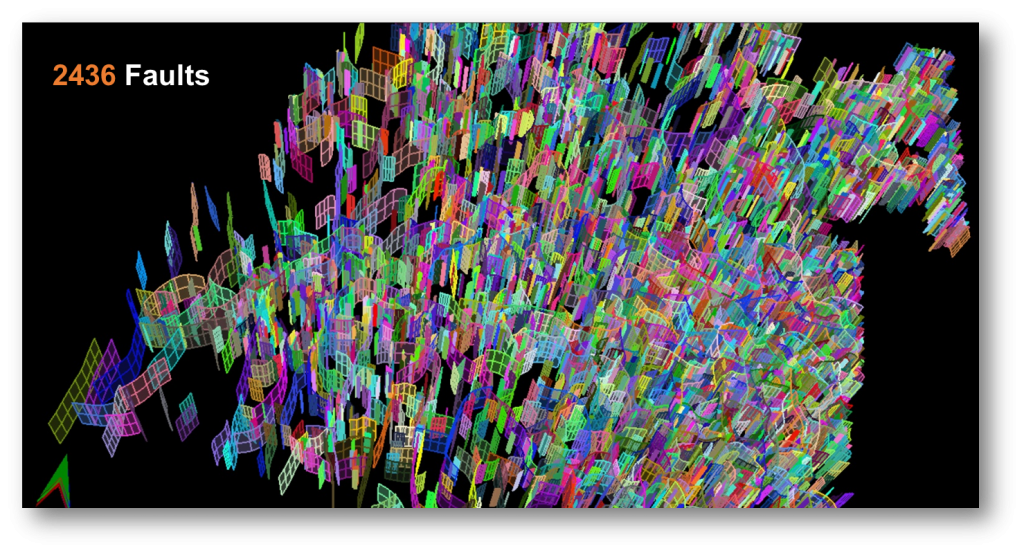
Fig. Fault model created by GES
Steps to perform Quick Stochastic Modeling in GES:
· Go to Quick Modeling Scenario → Quick Stochastic Modeling → One Button
· Basic Information:Input Model Name → Select Boundary → Select Stratigraphy Scheme → Select Well
· Fault Modeling: Select fault data → Click Run
· Horizon Modeling: Input Grid Name → Set I/J Increment/Number → Select Algorithm → Click Modeling → Select Layering Method → Set Number for each method according to Method Description → Click Layering
· Facies Modeling: Select log data for Discrete Logs → Click Block Wells → Select a zone in left of window → Select Algorithm → Set model parameter and carry out Variogram Analysis for the zone → Copy Parameter settings and paste to the rest zones or set parameters and algorithm for the rest zones →Click Run
· Petrophysics Modeling: Select log data for Well Logs → Select method for Average → Click Block Wells → Select a zone in left of window → Select Algorithm →Set model parameter and carry out variogram Analysis for the zone → Copy Parameter settings and paste to the rest zones or set parameters and algorithm for the rest zones → Click Run
Quick Deterministic Modeling
Quick deterministic modeling uses a rectangular grid, which is the second grid system in GES. In quick deterministic modeling, you can directly use 2D geological results, like surface result, facies map and well logs to generate a model. You don’t need to process data again, so it saves a lot of time. This method is based on rich 2D results, so it suits for the middle and late stages of oilfield development. In rectangular grid, you can do local refine to meet the different accuracy requirements.
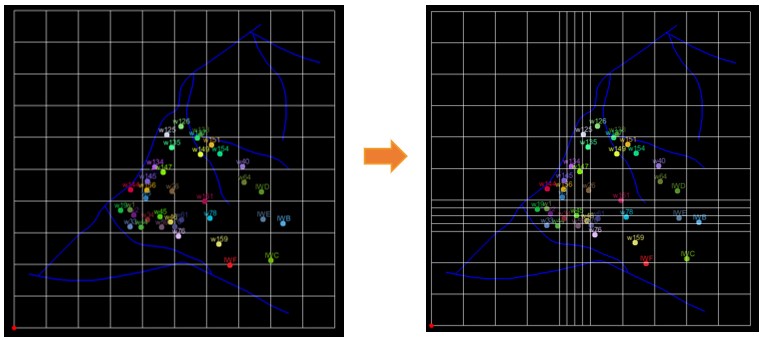
Fig. Rectangular Grid (left) and after local refine (right)
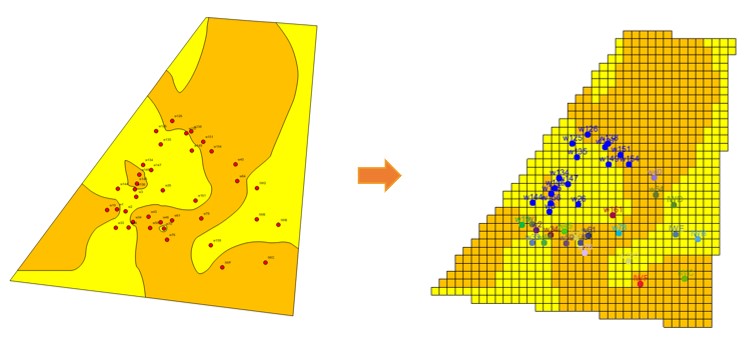
Fig. Facies map (left) and facies model surface (right)
Steps to perform Quick Deterministic Modeling in GES:
· Go to Quick Modeling Scenario → Quick Deterministic Modeling
· Click Create Model →Input Model Name →Click OK
· Go to Model pane →Click the model you just create →Click Rectangular Gridding on ribbon bar → Import Boundary or draw a new boundary → Open Rectangular Grid Settings window on window bar
· Click Quick Modeling on ribbon bar → Select data for Stratigraphy → Check Petrophysics Data for Modeling → Select log data for well logs
· Structure Modeling: General Settings → Well Settings → Fault Settings
· Facies Modeling: Select Facies map for each zone
· Petrophysics Modeling: Select Algorithm → Click Run All